In the realm of emerging infectious diseases, the Nipah virus stands out as a particularly deadly and mysterious threat. First identified in 1998 in Malaysia, Nipah virus has periodically reemerged in South and Southeast Asia, sparking concern among public health officials and researchers alike. This article delves into the origins, symptoms, transmission, and prevention of Nipah virus, shedding light on this enigmatic pathogen.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe Origins of Nipah Virus
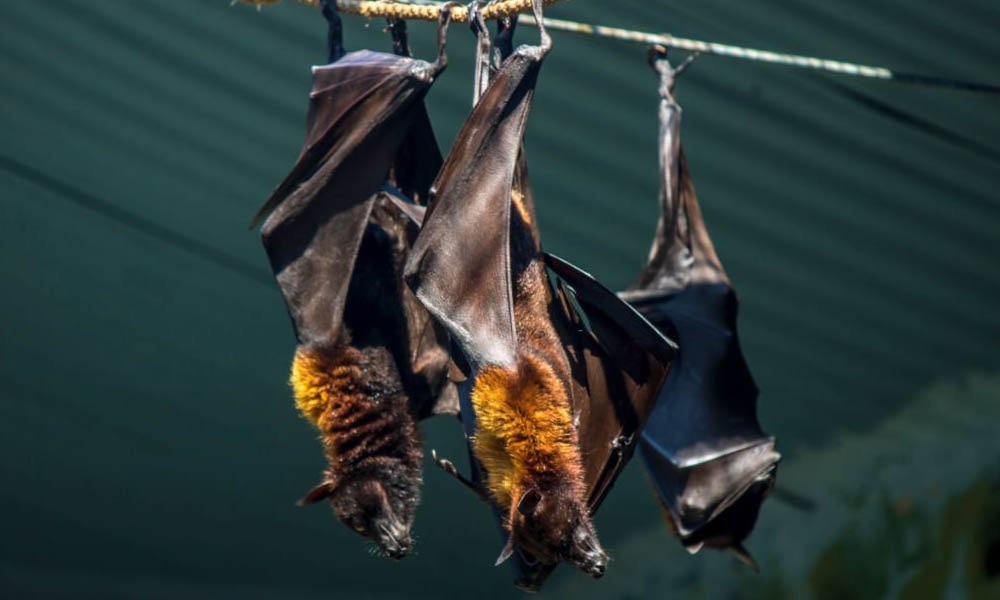

Nipah virus (NiV) takes its name from the Malaysian village of Sungai Nipah, where the virus was initially identified in 1998. It belongs to the family Paramyxoviridae and the genus Henipavirus. Bats, particularly fruit bats (Pteropus spp.), are considered the natural reservoirs of Nipah virus, meaning they carry the virus without falling ill themselves.
The virus can be transmitted to other animals, including pigs, which act as intermediate hosts. In outbreaks, humans can become infected through direct contact with infected animals or, more commonly, through the consumption of contaminated food or beverages. Person-to-person transmission can also occur, making Nipah virus a significant public health concern.
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation
Nipah virus infection can result in a wide range of symptoms, which can vary in severity. The incubation period typically ranges from 4 to 14 days. Common initial symptoms include fever, headache, muscle pain, vomiting, and sore throat. Respiratory symptoms can also occur, and in severe cases, individuals can progress to encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), which often leads to altered consciousness, seizures, and a high mortality rate.
One of the distinctive aspects of Nipah virus infection is its ability to cause acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), a severe and often fatal condition that affects the lungs. This characteristic sets Nipah virus apart from other zoonotic viruses and underscores the need for vigilance in its prevention and control.
Transmission
The transmission of Nipah virus to humans primarily occurs through close contact with infected animals or contaminated materials. This can happen in several ways:
- Consumption of Infected Food or Beverages: In regions where Nipah outbreaks have occurred, consuming raw date palm sap contaminated with bat saliva or urine has been a common route of infection.
- Direct Contact with Infected Animals: People in close contact with infected pigs or other animals can contract the virus through respiratory secretions or bodily fluids.
- Person-to-Person Transmission: Although less common, Nipah virus can spread from an infected person to others through close contact, especially in healthcare settings.
Prevention and Control
Preventing Nipah virus infections involves a multifaceted approach:
- Avoid Contact with Infected Animals: Farmers and individuals involved in animal husbandry should take precautions when handling sick animals and ensure proper biosecurity measures are in place.
- Safe Food Practices: Avoid consuming raw date palm sap and ensure proper hygiene in food preparation and handling, especially in regions where Nipah outbreaks have occurred.
- Infection Control in Healthcare Settings: Healthcare workers should implement strict infection control measures when caring for Nipah virus patients to prevent nosocomial transmission.
- Surveillance and Rapid Response: Early detection and reporting of Nipah virus cases are essential to contain outbreaks promptly.
- Vaccine Research: Ongoing research aims to develop vaccines and treatments for Nipah virus, which could be critical in preventing future outbreaks.
Nipah Virus Diagnosis and Treatment

Diagnosis: Diagnosing Nipah virus infection can be challenging, as its early symptoms are similar to many other common illnesses. Laboratory tests, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays, can confirm the presence of the virus in blood or other body fluids. Chest X-rays and other imaging may be used to assess lung involvement in severe cases.
Treatment: There is no specific antiviral medication for Nipah virus, so treatment primarily focuses on supportive care. Patients with severe respiratory distress or encephalitis may require intensive care, including mechanical ventilation. Research into potential treatments and therapies, such as antiviral drugs and monoclonal antibodies, is ongoing, but no widely accepted treatment protocols exist as of the latest information available.
Impact on Communities and Economies
Nipah virus outbreaks can have profound consequences on affected communities and economies. These impacts extend beyond the immediate health risks:
Economic Impact: Outbreaks can lead to the culling of large numbers of pigs, which can devastate the livelihoods of farmers and disrupt the pork industry. Tourism may also suffer due to fear of infection.
Community Disruption: Fear of the virus and public health measures to control its spread can disrupt daily life in affected areas. Quarantines, school closures, and travel restrictions can strain communities.
Psychological Toll: Nipah virus outbreaks can lead to psychological distress among affected individuals and communities. The fear of infection and the loss of loved ones can have lasting effects on mental health.
Global Preparedness and Research
Given the unpredictable nature of Nipah virus outbreaks, global preparedness and research efforts are crucial:
International Cooperation: Collaboration among countries and international organizations is essential for monitoring, reporting, and responding to potential outbreaks. Timely information sharing and coordination can help prevent the spread of the virus.
Vaccine Development: Research into Nipah virus vaccines continues, with several candidates in various stages of development. The availability of a safe and effective vaccine would be a significant milestone in controlling the virus’s spread.
One Health Approach: The One Health approach, which recognizes the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health, is increasingly important in understanding and mitigating Nipah virus outbreaks. It emphasizes collaboration between human and veterinary medicine, wildlife ecology, and environmental science.
Lessons from Past Outbreaks
The history of Nipah virus outbreaks offers valuable lessons for both public health officials and the global community. These outbreaks have highlighted the need for prompt and coordinated responses, improved surveillance, and increased awareness of zoonotic diseases. By analyzing the factors that contribute to Nipah virus emergence and spread, we can better prepare for future outbreaks and minimize their impact.
Nipah Virus and Bioterrorism Concerns
Due to its high mortality rate and potential for person-to-person transmission, Nipah virus has raised concerns about its potential use as a bioterrorism agent. The virus’s ability to cause severe respiratory distress and encephalitis makes it a formidable candidate for misuse. As a result, governments and international organizations are actively monitoring and securing laboratory samples of Nipah virus to prevent unauthorized access and misuse, emphasizing the importance of biosecurity measures and international cooperation in bioterrorism prevention.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Nipah virus?
Nipah virus (NiV) is a zoonotic virus that can be transmitted from animals to humans. It was first identified in Malaysia in 1998 and is known for its high mortality rate.
What are the natural reservoirs of Nipah virus?
Fruit bats, particularly those belonging to the Pteropus genus, are considered the natural reservoirs of Nipah virus.
How is Nipah virus transmitted to humans?
Nipah virus can be transmitted to humans through direct contact with infected animals, consumption of contaminated food or beverages, and person-to-person transmission, especially in healthcare settings.
What are the symptoms of Nipah virus infection?
Symptoms of Nipah virus infection can include fever, headache, muscle pain, vomiting, sore throat, respiratory symptoms, altered consciousness, seizures, and encephalitis (inflammation of the brain).
What is the incubation period for Nipah virus?
The incubation period for Nipah virus typically ranges from 4 to 14 days after exposure.
Is there a specific treatment for Nipah virus?
There is no specific antiviral treatment for Nipah virus infection. Supportive care, including mechanical ventilation in severe cases, is the primary approach.
How can Nipah virus be diagnosed?
Laboratory tests, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays, can confirm the presence of Nipah virus in blood or other body fluids.
Can Nipah virus be prevented?
Prevention measures include avoiding contact with infected animals, practicing safe food handling, implementing infection control in healthcare settings, and supporting ongoing research into vaccines and treatments.
Is there a vaccine for Nipah virus?
As of the latest information available, there is no licensed vaccine for Nipah virus, but research into vaccine development is ongoing.
Can Nipah virus outbreaks be predicted?
Nipah virus outbreaks are challenging to predict, but monitoring and surveillance in areas with a history of outbreaks can help with early detection and response.
Where have Nipah virus outbreaks occurred?
Nipah virus outbreaks have occurred primarily in South and Southeast Asia, including countries like Malaysia, Bangladesh, India, and Singapore.
What is the global impact of Nipah virus outbreaks?
Nipah virus outbreaks can have significant economic and social impacts, including disruptions to agriculture, tourism, and community life.
Are there any specific precautions travelers should take in Nipah-affected regions?
Travelers should be aware of the risk and follow local health advisories. They should avoid consuming raw date palm sap and take hygiene precautions with food and water.
What is the One Health approach in relation to Nipah virus?
The One Health approach recognizes the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health and is essential for understanding and mitigating Nipah virus outbreaks.
How can I stay informed about Nipah virus developments?
To stay informed about Nipah virus developments, you can follow updates from reputable health organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and your country’s public health department. It’s important to rely on credible sources for accurate information.
What measures are taken to control Nipah virus outbreaks?
Controlling Nipah virus outbreaks involves a range of measures. These include isolating infected individuals, tracing and monitoring contacts, implementing quarantine measures when necessary, and enhancing infection control practices in healthcare settings. In areas where Nipah outbreaks are common, public health authorities may also conduct culling of infected animals to prevent further transmission.
What research is being conducted to better understand Nipah virus?
Researchers and scientists are actively studying Nipah virus to enhance our understanding of the virus and develop effective preventive measures. Ongoing research areas include the development of vaccines, antiviral drugs, and diagnostic tools. Additionally, scientists are investigating the genetic diversity of Nipah virus strains and its potential for mutation, which can impact its virulence and transmission dynamics.
These FAQs provide essential information about Nipah virus, its transmission, symptoms, prevention, and ongoing research efforts to combat this deadly pathogen. Staying informed and following recommended precautions are key to reducing the risks associated with Nipah virus outbreaks.
Conclusion
Nipah virus is a formidable and lethal pathogen that emerges periodically, causing outbreaks in South and Southeast Asia. Understanding its origins, symptoms, and modes of transmission is crucial for effective prevention and control. Public health measures, such as avoiding contact with infected animals, practicing safe food handling, and ensuring rigorous infection control in healthcare settings, are vital in mitigating the threat of Nipah virus. Continued research and surveillance efforts remain essential to stay one step ahead of this enigmatic virus and protect public health.


